LiDAR stands for Light Detection and Ranging, and is a technique that we encounter in everyday life. But what exactly is it, and how do we use it?
What is LiDAR?
LiDAR is a technology that emits light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure variables from a distance. This technology can be used to create a high-resolution map of the Earth, and is often used in geography, seismology, and other fields.
Advantages
LiDAR has many advantages over other similar technologies. First, it is not affected by atmospheric conditions like fog or smoke. Second, LiDAR can provide very precise measurements, with greater accuracy than technologies like radar or sonar.
Applications of LiDAR
LiDAR technology is used in a wide range of applications, from agriculture to archaeology, from forest management to autonomous vehicles. In all these applications, LiDAR enables detailed measurements that can be analyzed in real time or afterward.
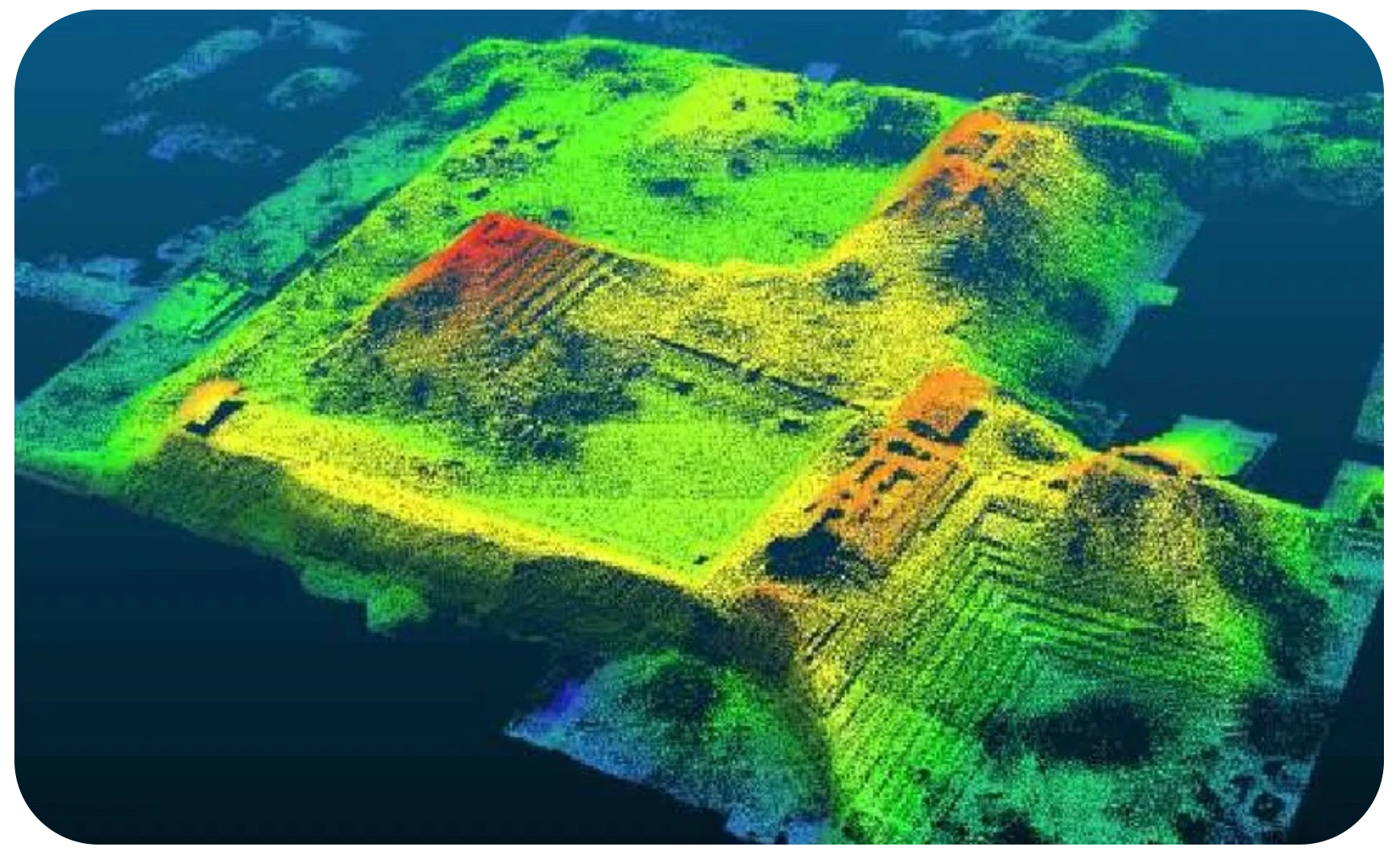

Through airspace LiDAR scanners, it is possible for archaeologists to find entire lost cities in the jungle.
Technical explanation of LiDAR
Essentially, LiDAR works by emitting pulses of light and then measuring the time it takes for the light to return to the sensor.
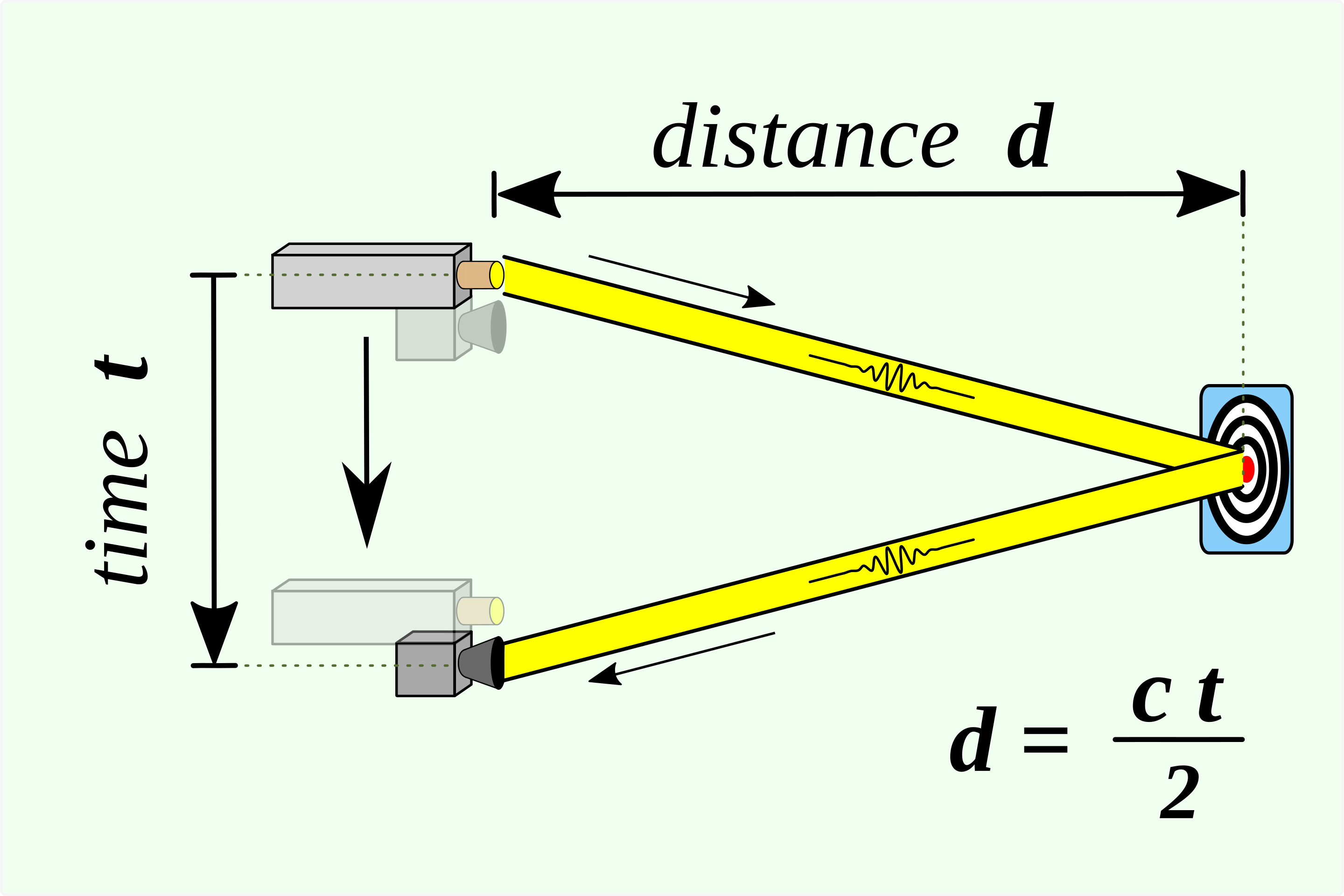
How is the distance measured?
Time of Flight Principle To measure distances, LiDAR uses a principle known as “Time of Flight”. This principle is based on the speed of light. When a pulse of light is emitted, it travels at a constant speed. The time it takes for the light to be emitted, hit an object, and return to the sensor can be converted into distance measurements.
How does the LiDAR scanner work?By means of light pulses The LiDAR scanner works by emitting thousands of these light pulses per second in a specific pattern. By means of light pulses The LiDAR scanner works by emitting thousands of these light pulses per second in a specific pattern. The LiDAR scanner works by emitting thousands of these light pulses per second in a specific pattern. By measuring the return time of each pulse, and knowing the angle and height of the scanner, a detailed 3D map of the environment can be created.
Example of Applied Distance Measurement
