In the Netherlands, about 1800 kilotons of waste are landfilled every year that has to be processed (sorted, ground, incinerated or composted).
“In the process of waste disposal, the risk of fire is considerable.
This is also evident from the number of (large) fires that occur annually at waste processors.
There are more than 50 of them and the damage is often extensive: >1 million.
As a result, insurers don’t line up to insure the industry or they force you to have very high deductibles; from a ton to a million euros,” says Elias Nieuwenhuis of the Association of Waste Companies.
Nieuwenhuis was one of the speakers at the seminar ‘Waste processing in 2016’, organised by and for the Register of Risk Experts.
Nieuwenhuis: “The complete prevention of fires at a waste processing company is an illusion. That’s never going to work. Nevertheless, the waste sector must do everything possible. Heating in waste heaps is one of the biggest risks. The heat-sensitive waste must be processed as quickly as possible, preferably within a day. In addition, measures should be taken to identify temperature increases in waste as soon as possible. But due to the many negative conditions at waste companies, such as moisture, dust and the height of the halls, this is not easy.”
Some waste processors have their fire risk well under control.
One of these companies, the Nijmegen ARN, is hosting the seminar.
Waste processing company ARN receives no less than 550,000 tonnes of waste every year.
About half of it is incinerated in one of the two state-of-the-art incineration lines.
The remaining waste is recycled elsewhere, whether or not after processing at ARN.
With the incineration process, ARN produces electricity (which is supplied to the public grid) and heat for two large residential areas and the adjacent waste treatment plant.
What is relatively new is that ARN uses the fermentation of organic waste to upgrade biogas to natural gas quality.
This is where the regional buses run.
Risk thinking determines the effectiveness of the solution
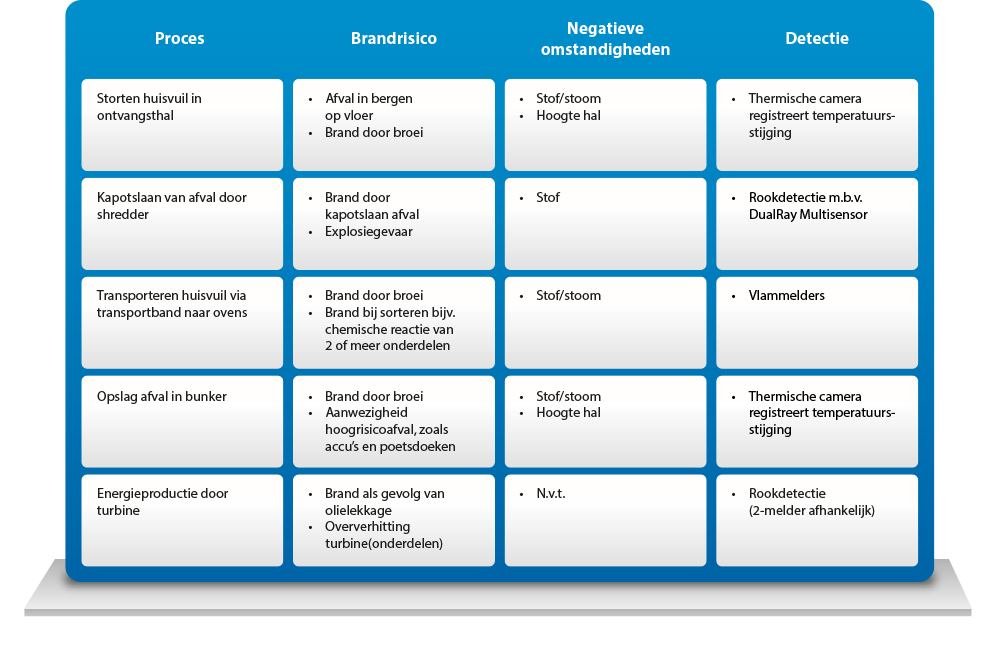
Only when you, as a waste processor, are well aware of your risks, can you take effective measures. ARN has carefully mapped out the risk moments and positions with regard to fire. “Every year, we carry out a broad risk assessment. This includes the risk of fire, but also, for example, the risk of negative publicity,” says Harrie Arends, executive secretary at ARN. Based on the risk inventories, we have not only taken technical measures, but also many organisational measures.” During the seminar at ARN, it quickly became clear that the risk of fire was present throughout the entire waste processing process. For example, waste can start to brew, for example in the hall where garbage trucks dump the household waste, the bunker with the waste storage and on the waste conveyor belts. There is also a risk of fire and explosion at the shredder installation that smashes the waste. In the hall with the turbine (where the heat from the incinerators is converted into electricity), a fire can occur due to overheating in the turbine itself or due to oil leaking. Almost every waste processor has to deal with similar risks and the same negative conditions.
Technical measures at ARN
ARN itself has a relatively new, certified fire alarm system.
The installation is quite large.
There are more than 1000 detection points and 200 controls.
An important part of the installation is the (user-friendly) management system.
Erik Poulussen, Account Manager at Mactwin, explains: “This allows the entire system to be operated and managed from one central point. If there is a fire alarm, you can see exactly which detector has been activated on a map. The fire brigade will also receive the exact location of the fire alarm. This is valuable information to determine the right plan of attack. In addition, we have set up flashlight areas so that they can also visually trace the location.”
In order to quickly identify a fire, ARN works with various detectors.
“Depending on the type of fire, the negative conditions present and the process, we have chosen a suitable detector together with ARN (see overview). In addition, cameras have been installed in many (high-risk) processes, the images of which are sent to ARN’s control room. “In this way, all (fire-sensitive) processes are monitored from the control room. Sometimes the cameras are also supportive of the process. For example, the crane operators use camera images to dump waste into hoppers that are out of sight of the operator with large grabs.”
Furthermore, an extinguishing system is of great importance to extinguish or reduce the size of a (starting) fire so that the damage can be limited. Poulussen: “ARN has a sprinkler system in use in many places, which is controlled by the fire alarm system. In the turbine hall, a high-pressure water mist system in the casing of the turbine and a foam extinguishing system in the hall were chosen. In the event of a fire alarm, the machines and ventilation are also stopped and compartments are automatically closed.”
The measures mentioned above at ARN are working to our full satisfaction.
Thanks to the stable and reliable detection system, several fires have already been prevented or extinguished in the early stages.
In order to guarantee the continuity of the measures taken, Mactwin has trained all ARN operators and support staff to become managers of the fire alarm system.
“Together with ARN employees, we also carry out a bi-weekly check-up and we carry out preventive maintenance every year in accordance with NEN 2654,” Poulussen explains.
Organisational measures at ARN
Finally, speakers and risk experts present emphasise the importance of organisational measures.
They are also well represented at ARN.
Bart Wattenberg, safety expert at ARN, explains that there is a strict safety protocol in place, as is a highly professional safety organisation that works closely with the fire brigade.
The contacts with the fire brigade are more than good.
They know the company and the site well (even use it regularly for their own exercises) and know that ARN has a modern, reliable fire alarm system that quickly guides them to the right location in the event of a fire.
Furthermore, there are maintenance protocols for the machines that are also strictly followed, random checks are carried out on the intake of waste and the waste is disassembled upon arrival.
The latter to prevent overheating.
